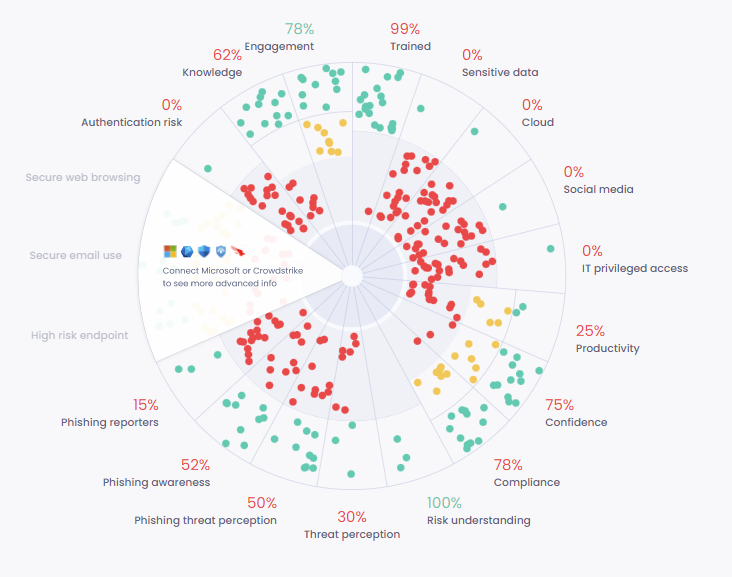
On the Human Risk Intelligence dashboard, the central wheel chart breaks down the security knowledge and behaviours of all employees. Filters can be applied to show the values for individual departments or risk levels.
TRAINING
- Knowledge
Employee’s knowledge of security policies and recommendations. Calculated based on questions asked in training - Engagement
Employee’s level of engagement with security training. - Trained
Percentage of employees who have completed the training they’ve been enrolled in. Based on a 180-day window.
ACCESS
- Sensitive Data
Employees handling sensitive data (including personal information, financial records, intellectual property and employee records). This data is collected from initial assessment survey during training.
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of users who frequently or sometimes handle sensitive data. - Cloud
Employees routinely accessing cloud services
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of users who frequently access cloud services. - Social Media
Employees using social media for work
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of users who frequently use social media for work purposes - IT Privileged Access
Employees with privileged access to IT systems
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of users who have privileged access to IT systems
ATTITUDES
- Productivity
How far employees feel able to work productively whilst following security policies and recommendations
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of users who have a severe productivity impact resulting from security measures - Confidence
This metric captures how many employees have the expected (and necessary) level of security knowledge. The higher the Knowledge value, the more employees possess this knowledge and can be expected to use it in real threat situations
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of users who feel generally unable to carry out security guidance - Compliance
How confident employees feel in their ability to work securely
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of employees who generally do not intend to comply with security guidance - Risk Understanding
How well employees understand the risks associated with poor security behaviors
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of employees who may not understand that security behaviors they’ve been trained on are essential to limiting risk - Threat Perception
How far employees recognise the seriousness of cybersecurity risks
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of employees who have a limited affective response to cybersecurity risk. These employees are not likely to internalise security behaviors
PHISHING
- Phishing threat perception
The extent to which the threat of phishing is perceived as serious across the organisation
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of users who chose not to complete additional phishing training when made aware of their vulnerability to phishing attack - Phishing Awareness
Employees’ ability to identify phishing emails
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of employees who are highly vulnerable to compromise by a phishing attack - Phishing Reporters
How likely employees are to report a phishing email
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of employees who are unlikely to report phishing emails if they spot them
BEHAVIOUR DATA
This data requires integrations with third party systems (DLP logs, GraphAPI, Defender, Sentinel, etc).
The metrics will appear in the wheel chart according to the data made available by your integration settings:
Graph API Features
- Email Fatigue Risk
Employees whose count of received emails significantly exceeds the organizational average. These employees may be more vulnerable to phishing attacks
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of users who are tagged as ’email fatigue’ by the tagging engine - Frequent Cloud Services Use
Employees who use cloud services for their work
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of users who are tagged as ‘cloud service use’ by the tagging engine
- Frequent Social Media Use
Employees who use social media platforms for their work
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of users who are tagged as ‘social media use’ by the tagging engine - Frequent Login Failures
Employees logging significantly more failed sign-in events than is normal across the organization. These employees are more likely to adopt poor password-management practices
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of users who are tagged as ‘authentication risk’ by the tagging engine
- Device at risk
Employees whose devices may be non-compliant or jailbroken
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of users who are tagged as ‘device at risk’ by the tagging engine - Is Manager
Employees who directly manage at least one person
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of users who are tagged as ‘is manager’ by the tagging engine. - Administrator Role
Employees assigned a Global Administrator or Billing Administrator role within the organization
When clicked: the User Performance grid populates with a list of users who are tagged as ‘administrator role’ by the tagging engine. These employees are possible targets to attackers to have access to the organisation systems